Digital entertainment – programs that put a serious load on the central processor. This component of the computer begins to heat up when playing games for a long time and can exceed the standard temperature values. The latter, as a rule, range from 61°C to 73°C and depend on the type of CPU. In fact, the temperature of the processor should not exceed 80 ° C, otherwise, the user risks facing serious problems. Next, the causes of CPU overheating, as well as ways to help solve the problem, will be discussed in detail.
Processor types and heat ranges during gaming
The normative values of CPU heating directly depend on its model. In gaming machines, the component is able to withstand high temperatures. In this case, the range from 61°C to 73°C is considered safe.
If we take the Intel Core I9 gaming processor, it can work stably when heated up to 93 ° C. In this case, nothing will happen to the car. Many models are also equipped with a protective device that acts like an automatic machine, turning off the PC when it reaches an extreme temperature value. These, for example, include Ryzen from AMD.
If the user has suspicions about the likelihood of CPU overheating, then he should find out exactly the model of the device and look at its characteristics. The easiest way to do this is according to the documents received along with the purchased PC.
Why does the CPU heat up?
An increase in component temperature is a normal process during processor operation. Heating occurs due to the passage of current by the element. Electricity, in turn, is a source of heat. Running the game puts an increased load on the computer, which leads to power generation or overheating if there is any malfunction. The latter may appear in several cases.
| Процессор | Нормальный диапазон (°F) | Нормальный диапазон (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Intel Pentium Pro | 165.2°F – 186.8°F | 74°C – 86°C |
| Intel Pentium II | 147.2°F – 167°F | 64°C – 75°C |
| Intel Pentium III | 140°F – 185°F | 60°C – 85°C |
| Intel Pentium 4 | 111°F – 149°F | 44°C – 65°C |
| Intel Pentium Mobile | 158°F – 185°F | 70°C – 85°C |
| Intel Core 2 Duo | 113°F – 131°F | 45°C – 55°C |
| Intel Celeron | 149°F – 185°F | 65°C – 85°C |
| Intel Core i3 | 122°F – 140°F | 50°C – 60°C |
| Intel Core i5 | 122°F – 145.4°F | 50°C – 63°C |
| Intel Core i7 | 122°F – 150.8°F | 50°C – 66°C |
| AMD A6 | 113°F – 134.6°F | 45°C – 57°C |
| AMD A10 | 122°F – 140°F | 50°C – 60°C |
| AMD Athlon | 185°F – 203°F | 85°C – 95°C |
| AMD Athlon 64 | 113°F – 140°F | 45°C – 60°C |
| AMD Athlon 64 X2 | 113°F – 131°F | 45°C – 55°C |
| AMD Athlon 64 Mobile | 176°F – 194°F | 80°C – 90°C |
| AMD Athlon FX | 113°F – 140°F | 45°C – 60°C |
| AMD Athlon II X4 | 122°F – 140°F | 50°C – 60°C |
| AMD Athlon MP | 185°F – 203°F | 85°C – 95°C |
| AMD Athlon XP | 176°F – 194°F | 80°C – 90°C |
| AMD Duron | 185°F – 203°F | 85°C – 95°C |
| AMD K5 | 140°F – 158°F | 60°C – 70°C |
| AMD K6 | 140°F – 158°F | 60°C – 70°C |
| AMD K6 Mobile | 167°F – 185°F | 75°C – 85°C |
| AMD K7 Thunderbird | 158°F – 203°F | 70°C – 95°C |
| AMD Opteron | 149°F – 159.8°F | 65°C – 71°C |
| AMD Phenom II X6 | 113°F – 131°F | 45°C – 55°C |
| AMD Phenom X3 | 122°F – 140°F | 50°C – 60°C |
| AMD Phenom X4 | 122°F – 140°F | 50°C – 60°C |
| AMD Sempron | 185°F – 203°F | 85°C – 95°C |
| Average | 141.61°F – 164.18 °F | 60.89°C – 73.43°C |
Lack of ventilation
The CPU is most vulnerable to overheating if there is no airflow in the computer. Poor ventilation can be the result of improper placement of the device (close to the wall), lack of windows in the room, and many other factors. To remedy the situation, the user is advised to take a number of measures:
- Set up a cooling unit in the computer room. If the room is hot and there is no ventilation, then this will help extend the life of the processor, as well as other components of the PC.
- Install the system unit at a distance from the walls. Free zones should remain on each side of the device.
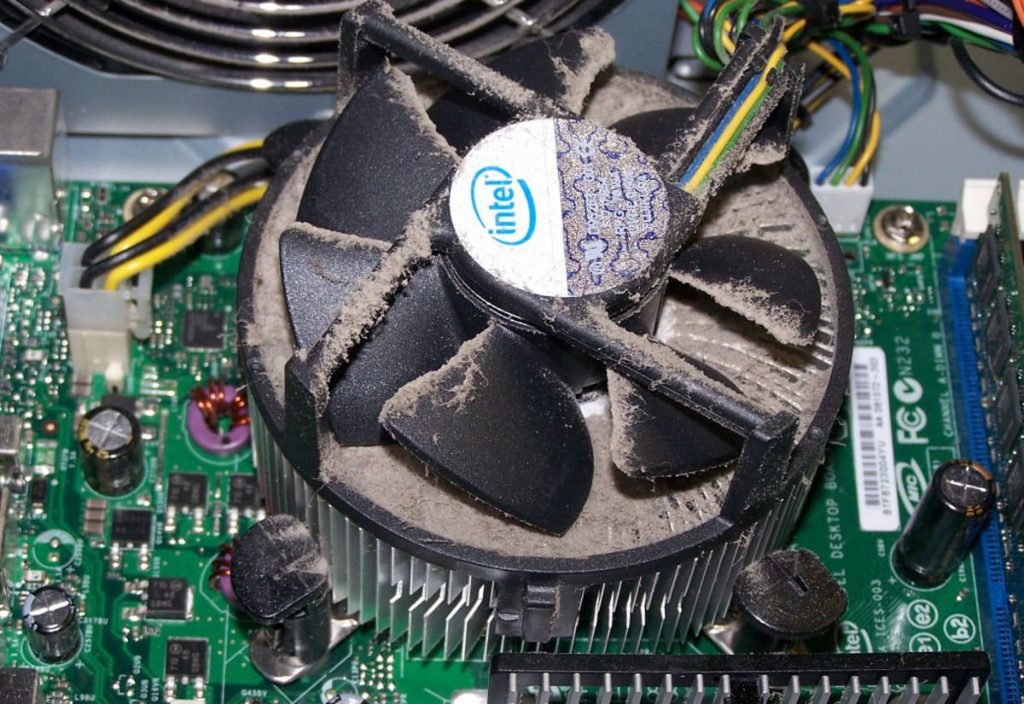
- Regularly check your PC for dirt. Dust is an allergen and can cause a short circuit, and excessive heating of the components of the system unit. As a rule, it settles on the blades of coolers and on radiators, reducing the rotation speed and heat dissipation.
- In the case of laptops, you should purchase a stand with a fan. It will increase the flow of air from below and will not allow the device to overheat.
Another way to keep the air circulating around the CPU area is to install additional coolers. Each fan will improve the airflow to the heating elements and prevent their failure. To add coolers to the system unit, the user has to perform several operations. First of all, the machine must be disconnected from the network and the removable side panel removed. After gaining access to the inside of the case, you need to inspect the attachment points and remove the plates with a tool (a screwdriver will do).
The installation of cooling elements is carried out taking into account the direction of air movement. It is necessary to make sure that the airflow goes inside the case, and not outside. After fixing the coolers, you need to connect them to the power supply. This requires special cables. One connector is connected to the fan, and the other to the controller or to the computer motherboard, depending on its model.
If the user is afraid to perform the manipulations described above on his own, then he should turn to professionals.
When choosing cooling fans, preference should be given to larger models, if their size fits the dimensions of regular places in the case. Such coolers will provide better air circulation and airflow to the components of the system unit.
Excessive load on the processor
Often modern games require a large amount of RAM. To access it, the PC will make every effort, which will lead to the heating of the processor.
If there are no signs of overheating, then you should not worry. At the same time, constant exposure of the CPU to extreme conditions will significantly reduce its service life and may lead to component failure. In order not to run into problems manifested in a PC failure, the user should take care of a more powerful “stuffing” for the machine.
Symptoms of CPU overheating
The easiest way to find out about exceeding the permissible temperature of the central processor is from information from a special application. There are many free programs that control the operation of individual parts of the PC. The user will be able to monitor the temperature in real-time and take action in time in case of a sharp increase.
One of the popular applications that you can try out in practice is “HWMonitor”. It is used by many programmers, designers, and gamers. The program will offer information about the temperature of the processor, hard drives, cooler rotation speed, and voltage. With such information, the user can easily understand whether everything is fine with the PC and which elements do not cope with the tasks assigned to them.
In addition to the software method of controlling overheating, there are several signs by which you can understand that the processor temperature exceeds the allowable values. The first is a reboot when you open or use any application. The second is the overheating alarm. And the third is the loud sound of the coolers. The latter, trying to increase the temperature, will work at the limit, which will lead to their excessive “buzzing”.
When to Consider Buying a New CPU
The processor should be changed at a constant maximum heating of the element. This process will indicate that the power of the component is not enough to solve the daily tasks of the user. Sometimes this can be the first sign of an imminent CPU failure.
It is not difficult to buy and install a CPU, but the expediency of such an event often raises questions. Since the processor can not cope with the proposed load, other components are also probably not up to the tasks that are set for them. Therefore, the user should think about replacing the entire system unit and choose it according to their needs.
Findings
Thus, the normal temperature for most processors during gaming is 61°C-73°C. If the component model does not provide for more heating, then the user should look for the cause. As a rule, the problem is solved by the correct location of the system unit, ensuring proper ventilation and timely cleaning of the case from dust. If these measures did not help, and the CPU continues to heat up, then the gamer should think about replacing the element or completely updating the computer.